The femtosecond lab is composed with two femtosecond lasers.
The Spitfire (6mJ - 30 fs) is equipped with a pulse shaper (Dazzler) and an ultra short pulses monitoring device (Frog). It is used for the following projects:
- Biomedical optics:
The in vitro optoporation in the MHz and kHz regimes is studied with this setup. Various cell lines have been tested to determine the ideal condition to perform transfection. Our research is mainly based on breast cancer, DMLA and cornea treatment. Cornea explants have also been used. In vivo experiments are upcoming, in partnership with Maisonneuve-Rosemont Hospital for the NanoEye project.
- Non linear optics
Please have a look on the Filamentation project for more information.
- Vertical and horizontal laser ablation
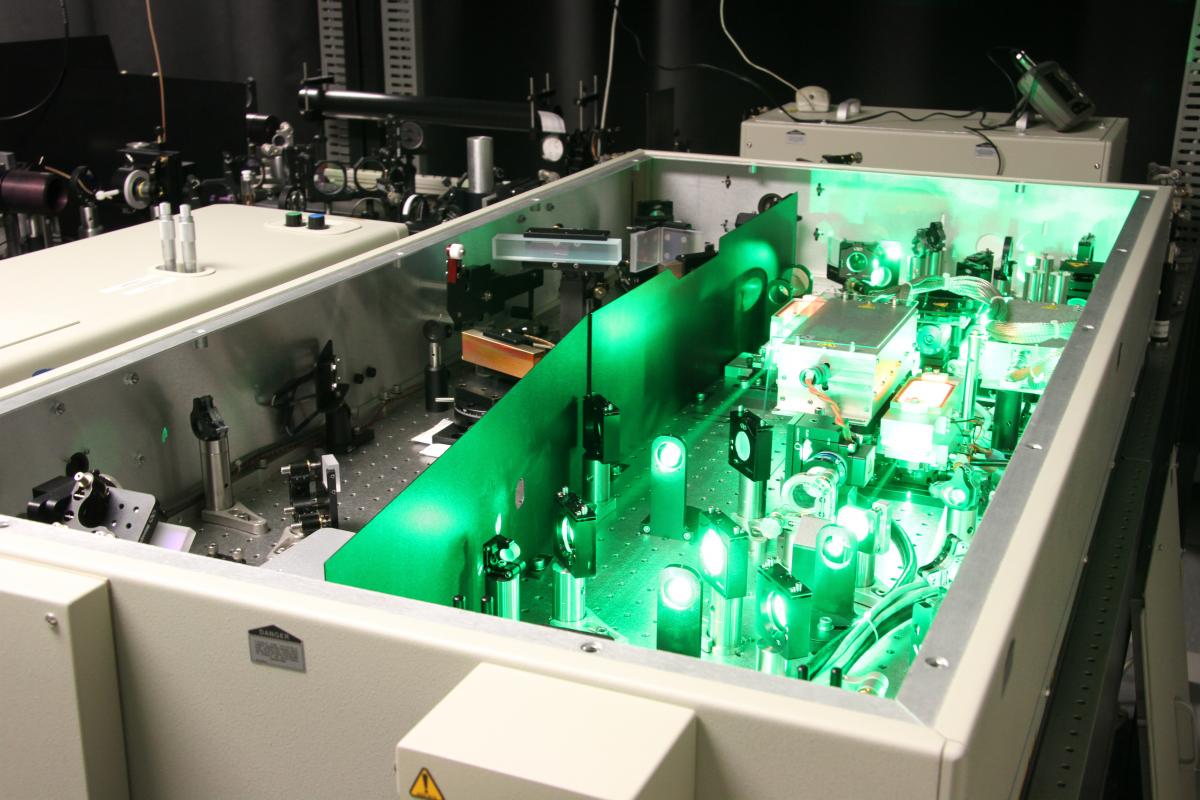
- Laser micro-machining
- Laser ablation (liquid environment, controlled atmosphere, or in vacuum)
- Fragmentation
The nanosecond lab contains 2 systems
The laser Nd:Yag nano BrillantB, Quantel (5ns, 1064nm - 1 J/pulse, 532nm 0,4 J/pulse - 266nm - 0,1J/pulse) is used for laser ablation and laser machining.

Our plasmonics lab contains several setups.
Thin layer measurement, SPR measurement (amplitude and polarization), spectral and angular nanoplasmonic measurement.
Source spectrum: 300 - 1600 nm
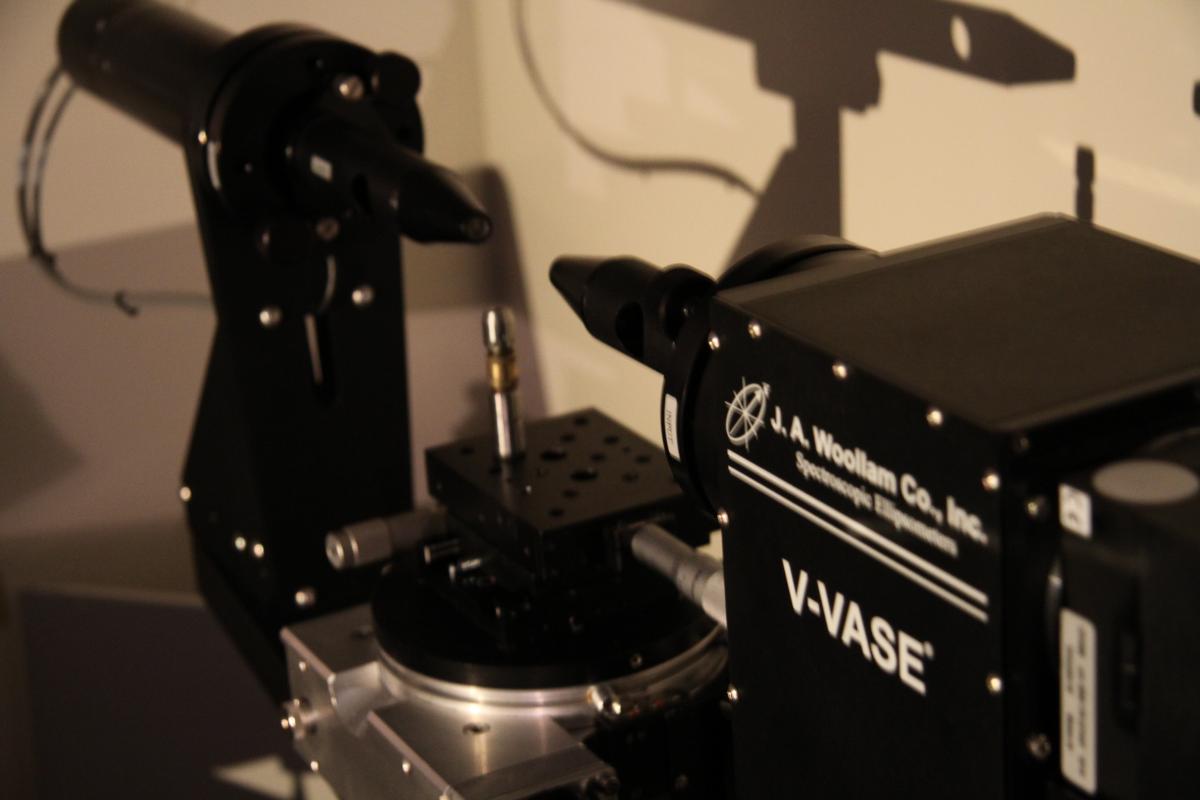

Biochemical applications (DNA detection, kinetic analysis, bacteria and virus detection)
Our biochemistry laboratory contains all the necessary equipment for various type of nanoparticle synthesis and cell culture.
Gold-Silver nanoparticles
- Quality control for the synthesis of AuAg NPs (size and composition)
- Multiplexed imaging
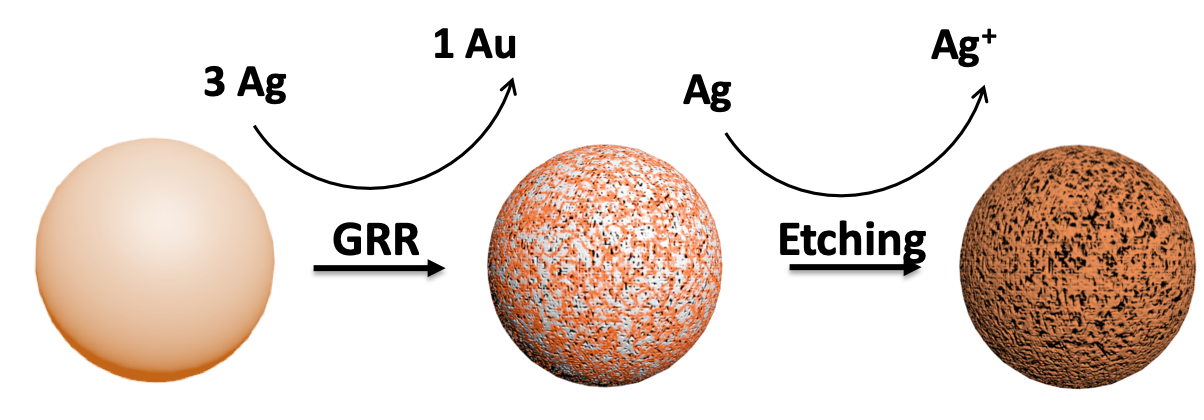
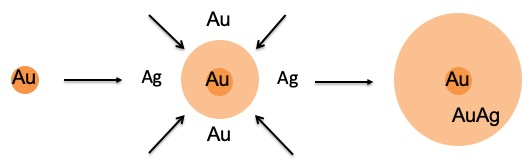

Porous nanoparticles synthesis
- NP morphology control
- Porosity design
- Biomedical application
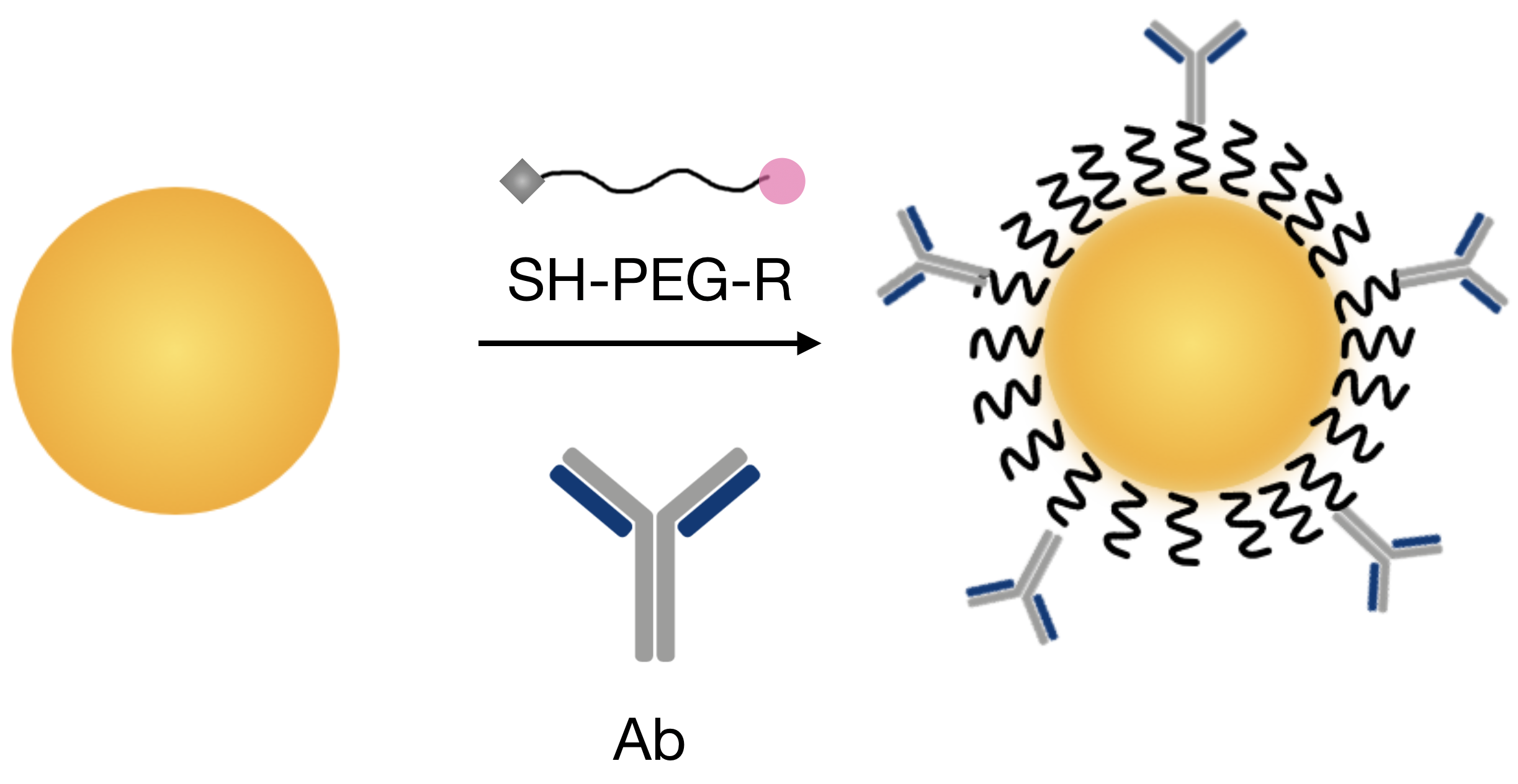
Principle:
Functionalisation is very crucial for using nanoparticles as biomarkers. The addition of polymers such as PEG onto the surface allows the NPs to become more biocompatible and water soluble, which are among the most important parameters for in vivo biomedical experiment. Then, covalent binding of antibodies is performed in order to have specific attachment on targeted cells. Various techniques can be found in the litterature. We have been mostly working with strategies involving PEG derived components (with NHS or Hydrazide), allowing stable binding with the antibody.
Our imaging lab is composed of various installation and allows for multiple imaging modalities, such as:
- Darkfield imaging
- Fluorescence imaging
- Back-scattering imaging
- Multi and hyperspectral imaging
- AFM




